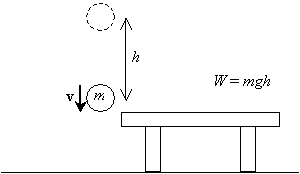
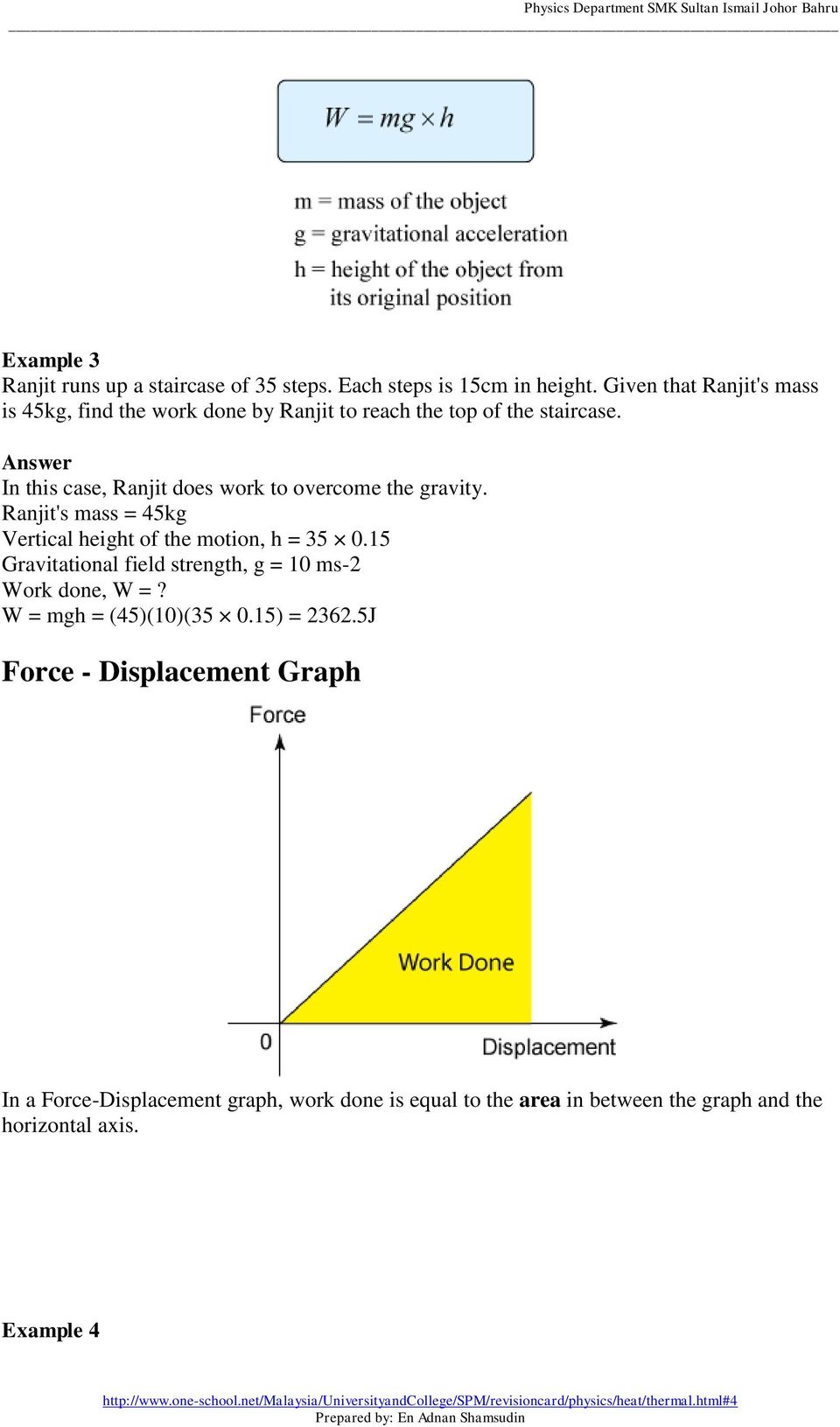
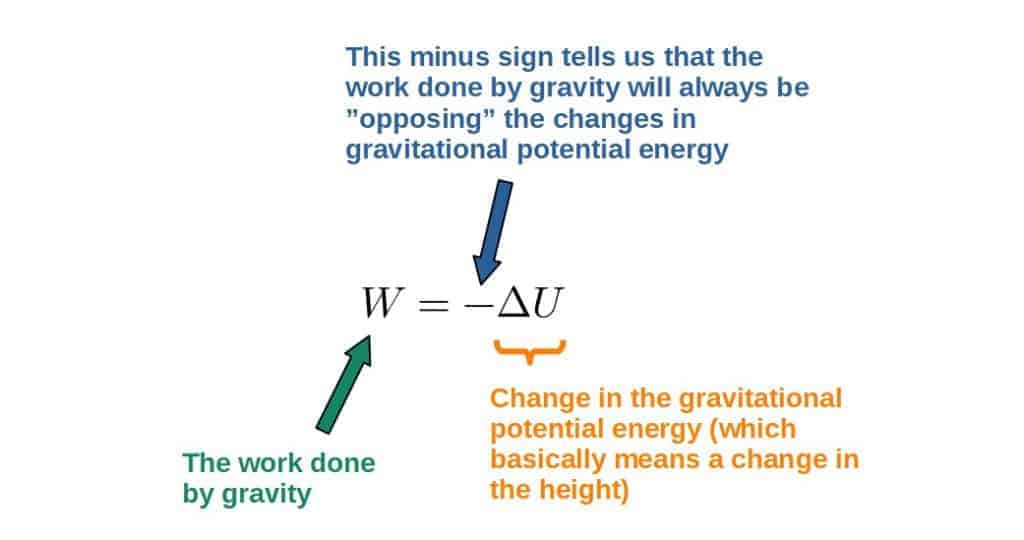
Potential Energy Concept The force on an object is the negative of the derivative of the potential function U This means it is the negative of the slope of the potential energy curve Plots of potential functions are valuable aids to visualizing the change ofGravitational potential energy is one type of potential energy and is equal to the product of the object's mass (m), the acceleration caused by gravity (g), and the object's height (h) as distance from the surface of the ground (the body) In this example, a 3 kilogram mass, at a height of 5 meters, while acted on by Earth's gravity would have 147 Formula (i) W = PE = mgh Solution W = mgh = x (98) x 10 = 1960J The work done to take an object of mass kg to a height of 10 m is 1960 J Question 7 A body of 05 kg thrown upwards reaches a maximum height of 5 m Calculate the work done by the force of gravity during this vertical displacement
Http Www Ponderisd Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 90 Work And Energy Pdf
Formula w=mgh
Formula w=mgh-W = mgh = ()(10)(15) = 300J Kuasa, P = W t P = 300 J s = 15 W External Link Interactive Animation — Share It — Work done, W = mgh or W = 1960 × 5 = 9800 J Example 6 A boy pulls a toy cart with a force of 100 N by a string which makes an angle of 60º with the horizontal so as to move the toy cart by a distance horizontally Calculate the work done Solution Given F = 100 N, s = 3 m, θ= 60º Work done is given by



Unit 4 Work And Energy Physics Project
We can derive the technical formula of the pump motor according to the principle of energy conservation The effective work done by the pump is W=Mgh (send a certain weight of medium to a certain height h, h is the lift) M is the mass of water m = ρV (ρ is the density of the medium, the volume of the V medium) V = Qt (Q represents the flowW = mgh Where, W = work done g = acceleration due to gravity h = height of free fall If the angle between gravitational force and direction of motion is 𝚹, then work done due to gravity is given by W = mgh cos 𝚹 So if an object is moving in horizontal direction on the surface of earth, then work done by gravity is 'zero'The magnitude of the falling body depends on the mass, gravitational constant and height from which it is falling The work done by gravity is given by the formula, Wg = mg (∆ h) Where, m = mass, g = gravity, h= height
So potential energy U = W = mgh #6 cragar 2,552 3 i thought work was the change in kinetic energy and work is the integral of F*s #7 ImAnEngineer 9 1 cragar said i thought work was the change in kinetic energy and work is the integral of F*s Its calculated by the following equation; El geopotencial es el Trabajo necesario para elevar la unidad de masa a una altura dada (recordar la formula W = mgh) En la fórmula hidrostática y otras similares si usamos altitud geopotencial en lugar de altitud métrica g pasa a ser una constante Fue Bjerknes con sus colaboradores quien propuso utilizar el geopotencial con esa intención
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ Solve for h P=mgh Answer choices H=Pmg H=pg/m H=p/mg H=PmgWhat is W MGH?Work is the energy transferred into or out of a system through the action of a force Work done against gravity can be found using the equation Work equals Force times height or W = Fh Since F = mg we can use the equation W = mgh (m = mass, g = gravity, or 981 m/s² and h = height)



Malaysia Pmr Spm Student S Learning Portal Provides Free Notes E Books References Formula List For Teachers Students For Tuition Or School Study Purposes



Solved In A Lab Investigation One Group Of Students Group A Measures The Speed Of A 0 1 Kilogram Car At 2 5 M Sec At The Bottom Of A Hill Anoth Course Hero
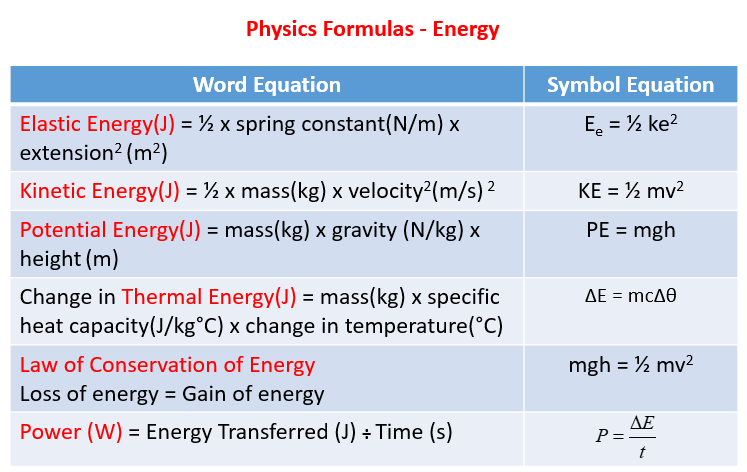
Find an answer to your question in chapter work and enrgy is it necessary that we have to use the formula W=mgh or is there any other formula to find height?Find the potential energy when the mass is 12 with a height of 24 and acceleration due to gravity of 98 This implies that;These formulae apply to all energy transfers, and in the case of objects in a uniform gravitational field, g, the WD = F x d = mg x h When this work is done on an object, which only raises it up, away from the earth, but gives it no KE, then the energy transferred to it can only be GPE So, therefore;




Work Energy Power September 00 Number Work If A Force Acts On A Body And Causes It To Move Then The Force Is Doing Work Pdf Free Download



Gravitational Potential Energy Zona Land Education
Work done against gravity can be found using the equation Work equals Force times height or W = Fh Since F = mg we can use the equation W = mgh Since F = mg we can use the equation W = mgh (m = mass, g = gravity, or 981 m/s² and h = height)Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it Solution for W=mgh equation Simplifying W = mgh Solving W = ghm W = F ∙s = mgh, W = mgh (3) mgh = 1 2 m v f 2 mgh = 1 2 m v f 2 v f 2 = gh 1 2 = 3 gh v f = √ 3 gh v f = √ 2 (98)(13)= 1596 m / s Ejemplo 3 Un bloque de masa M de masa 5 kg está suspendido por dos cuerdas Se dispara una bala de masa m= gr hacía el bloque, la bala se incrusta y el bloque se eleva una altura h=7cm respecto a su




Power Problems And Solutions Solved Problems In Basic Physics




Set 3 Problem Solving Classes S1 16 Studocu
Joanna84 joanna84 Physics Secondary School answered Transposing and Rearranging Formulas In a previous lesson we showed how to Solve Equations using the work down through the "Onion Skins" Method Knowledge of that lesson is needed as a background, before doing our lesson on Rearranging Formulas In our Transposing Formulas lesson we will review the use of the "Onion Skin" method, andVisit http//wwwudemycom/howyoucanbegoodatmathsandgreatatfractions/ for my new course or click here for a limited 50% discount!



1




W=mgh Where W =work (Joules), m = mass, g= gravity (981) and h = height of lift Dip (m) This is the distance the weights were moved below the zero point The zero point is automatically set after you press âokâ on the weight dialog on the palm application Itâs the starting position of the lift Adding equation 1 and equation 2 W = W 1 W 2 W = mgh mgh W W = 0 The work done by the gravitational force in the complete circle of the object is zero Therefore, the gravitational force is a protective forceWe use the same formula for work that you already know (Work = force × distance), but it's expressed in a slightly different form Force is written in the form mg, where m is mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity, 98 m/sec2 W = mgh Work against gravity mass acceleration due to gravity= × ×height




Gravitational Potential Energy Ppt Video Online Download



2
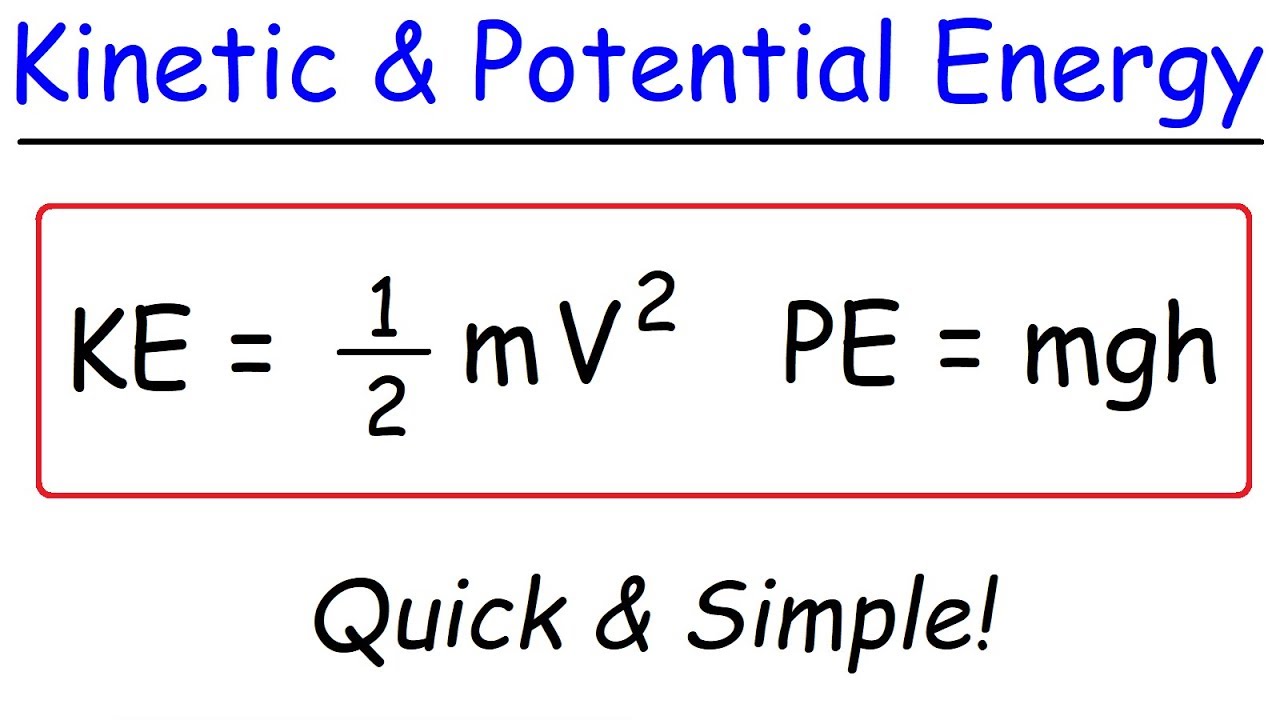
重力势能(gravitational potential energy)是物体因为重力作用而拥有的能量。物体在空间某点处的重力势能等于使物体从该点运动到参考点(即一特定水平面)时重力所作的功。重力势能的公式:Ep=mgh 。Gravity F = mg does work W = mgh along any descending path In the absence of other forces, gravity results in a constant downward acceleration of every freely moving object Near Earth's surface the acceleration due to gravity is g = 98 m⋅s −2 and the gravitational force on an object of mass m is F g = mgPE = Potential Energy m = Mass g = acceleration due to gravity h = Height Let's solve an example;



What Is Kinetic Energy Universalclass




What S The Difference Between Work And Potential Energy Wired
2 12,276 2 minutes read Gravitational potential energy is defined as the "energy of an object due to Earth's gravity"OR it is the product of the object's weight and heightIt is the most common example of PE Its formula is W = mgh It means the higher an object the higher will be its Gravitational PEW mgh, for g 15 PV nRT, for V 16 G F D, for D 17 6t 62s (3t 42s), for t 18 3c 5d 7d 6c, for d 19 Standardized Test Practice Four ninths of a number c increased by 4 is 18 less than one eighth times another number d Solve for c A c 3 9 2 d 31 1 2 B c 7 4 2 d 7 4 2 C c 3 9 2 d 49 1 2 D c 7 4 2 d 31 1 2 1 2 4 3 n 2 Solving Equations andTrabajo efectuado por la fuerzapeso Objetivo Resolver situaciones problemáticas de trabajo Considerando un cuerpo de masa m, lanzado verticalmente del suelo hacia arriba y alcanzando una




Illustration Physics Gravitational Work Potential Energy Stock Vector Royalty Free



Work
The formula for calculating the potential energy PE = mgh Where;I think the better question is "What does mgh stand for symbolically in physics and what is its significance?" Because this is my interpretation, I will answer the question in this fashion mgh is asking for the product of three variables "m" isRst by heat entering the system and second, by work done on the system Equations (2) and (3) are called the rst law of thermodynamics relating heat,




Work And Energy Part 2 Video Khan Academy



Physics Formulas Examples Solutions Videos Notes
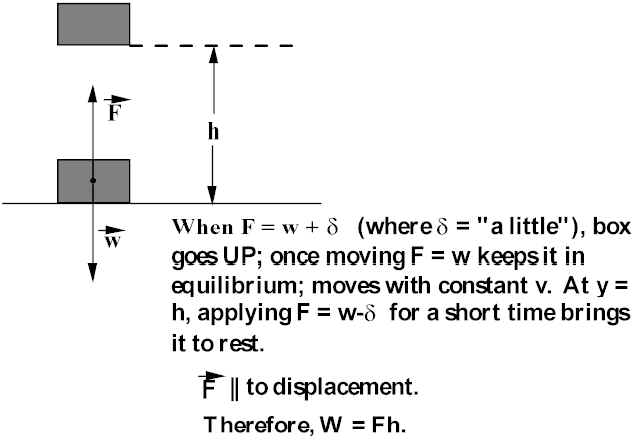
So long as the force and motion are in the same direction, the formula for work is W = (Force)(Distance) = F D The footpound combines a unit of force a pound with a unit of distance a foot and is thereby a unit of work or energy 1 footpound is the amount of work that must be done to raise a 1 pound weight by 1 footThus the formula to calculate the potential energy of the object is given by Potential energy = Mass × Acceleration due to gravity × Height Free Online CalculatorsThis equation is very similar to the kinematics equation v = v 0 2 2 ad v = v 0 2 2 ad size 12{v= sqrt {v rSub { size 8{0} } rSup { size 8{2} } 2 ital "ad"} } {}, but it is more general—the kinematics equation is valid only for constant acceleration, whereas our equation above is valid for any path regardless of whether the object moves



Unit 4 Work And Energy Physics Project



Work Energy And Friction
Example linear equation 1 Solve for J when 3𝐽𝐽−5 = 16 3𝐽𝐽−5 = 16 (target 5 then 3) 3𝐽𝐽−55 = 16 5 (Opposite of −5 is 5) 3𝐽𝐽= 21 3𝐽𝐽 3 = 21 3 (Opposite of ×3 is ÷3) ∴J = 7 (Check 3 × 7 −5 =16 )L'énergie potentielle de pesanteur (EPP) est l'énergie que possède un corps du fait de sa position dans un champ de pesanteur Comme pour toute énergie, son unité dans le Système international est le joule (J) Ce principe est utilisée pour certains systèmes de Stockage de l'énergie par Pompageturbinage d'eau à grande échelle (ex station de pompage turbinage de Bath CountyM = Mass = 12 g = acceleration due to gravity = 98 h = Height = 24




Unit 3 Energy And Systems Chapter 7 Machines




Error Using Mgh Intro To Physics Youtube
Rearrange the formula Ep = mgh, to find h In your case, displacement from the surface to a height h, the force (gravity) is pointing downwards and the displacement is upwards So the work is negative, W=mgh and the potential energy is PE=W= mgh It does not matter how you move the body between the two points, the work done by gravity is the sameSimple and best practice solution for W=MGH(M) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it



Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy Youtube



How To Derive The Formula Of Gravitational Potential Energy Mgh Dronstudy Questions
W= mgh The displacement over which the work is done equals the height of the lift (d = h)Formula for finding the heat that must be given to a body of mass "m" and specific heat "c" to increase its temperature a given amount Q = mLf W = mgh formula for total work done by the gravitational field upon a weight ΔEint = Q W formula for the first law of thermodynamics Derivation of w=mgh Asked by sanjeevrao2704 4th Jun, , 0843 AM Expert Answer If a body of mass m moves down from a height h, the force of gravity or weight acts on the body through a displacement h Thus, work




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics



Unit 4 Work And Energy Physics Project
mgh dimensional formula of mass is M¹ dimensional formula of g (acceleration due to gravity) is L¹ T² dimensional formula of height (length) is L¹ so dimensional formula of mgh will be = M¹ L²T² so LHS = RHS it means formulas are dimensionally correct Comment if you have any problemStudy free Science flashcards and improve your grades Matching game, word search puzzle, and hangman also available Power Formula We can refer to power as the rate at which we do work Also, it is the ratio of work and time Besides, we calculate it mathematically using this formula or equation Derivation of Power formula Power = unit of measure (Watt) W = work done by the body t = time taken to do the work Moreover, the standard unit of measuring power




Work N Energy Kilowatt Hour Force



Search Q Power Formula Tbm Isch
Equation (3), which is simply rearrangement of (2) is another way of saying that the internal energy can increase in two ways; 811 Equilibrium conditions If the state of an isolated system is an equilibrium state, this state does not change over time (Sec 244) We expect an isolated system that is not in an equilibrium state to undergo a spontaneous, irreversible process and eventually to reach an equilibrium state Just how rapidly this process occurs is a matter of kinetics, not thermodynamicsΔGPE = mgh, where Δ means 'a f




H Write The Equation For Kinetic Energy K Mrz I Chegg Com




Physics Home Basic And Important Formula S Of Physics Facebook
The work done by gravity on a falling object depends only on the total change in height, given by the formula W=mgh If an object is not falling (its height




Gravitational Potential Energy Definition Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



S3 Amazonaws Com Scschoolfiles 747 Ch 9 4 Gravitational Potential Energy Pdf




Chapter 4 Work Energy And Power



Q Tbn And9gctqsxto1cfyzcfby4veokitwilwpouun7wzspq7pgwhoqm9zuxd Usqp Cau



Cdn1 Byjus Com Wp Content Uploads 05 Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 4 Pdf



How Can We Say The Formula Of Potential Energy Equals Mgh Quora



Pmt Physicsandmathstutor Com Download Physics A Level Topic Qs Aqa Old Unit 2 Set B 2 1 energy work power ms Pdf




Pin By Prabhath Nalaka On Ramana Physics Formulas Physics Physics And Mathematics




Potential Energy Physics 12 Potential Energy In Grade 11 Physics We Looked At Gravitational Potential Energy In Grade 11 Physics We Looked At Gravitational Ppt Download



Http Www Ponderisd Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 90 Work And Energy Pdf



Work Energy Power Ib Physics Stuff



Simple Concepts Involving Work And Energy
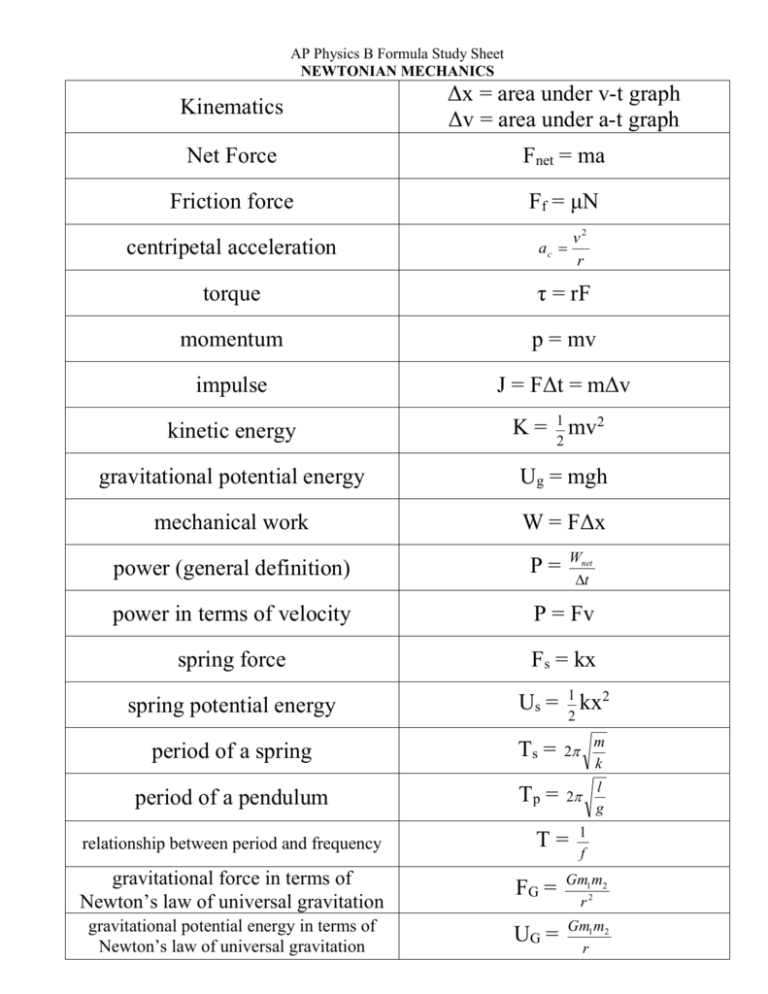



Ap Physics B Formula Study Sheet




Kinetic And Potential Energy




Gravitational Potential Energy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Gravitational Potential Energy Mammoth Memory Physics




Education Is The Key To Success Physics Class X Chapter No 8 Questions And Answessc Part 1 And 2




Power Problems And Solutions




Physics 2 10 Work Power Energy And Efficiency Flashcards Quizlet



Weight The Weight Of An Object Is Defined As The Gravitational Force Acting On The Object Unit Newton N Pdf Free Download



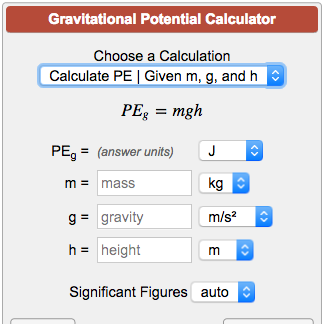
Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator




Gravitational Potential Energy Emedicalprep



Work Energy And Power



Kdagr Physics Science Theory Law And Mathematical Formula Equation Doodle Model In White School Education Mousepad Mouse Pad Mouse Mat 9x10 Inch Walmart Com Walmart Com




Here Is A Helpful Formula Sheet For Your Physics Class Physics



Http Www1 Lasalle Edu Didio Courses Phy105 Text Solns Ch 08 Pdf



Www Scasd Org Cms Lib5 Pa Centricity Domain 1441 Summary Sheet 6 Pdf



Energy Forces And Vectors




Work Physics Definition Formula How To Calculate W Diagram Examples




Potential Energy Formula And Sample Problem Pinoy Techno Guide



Http Www Physics Sfsu Edu Wman Phy111hw Lecture notes Chapter08numberdisclosed Pdf



Homework 3 Solutions




Gravitational Potential Energy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



1




Gravitational Potential Energy Derivations Formulas Examples



03 Power Energy Gravity




Ozark Dragon How Much Electrical Power Can Bagnell Dam Produce Part 3




Physics Formulas Ap Physics Physics




Ppt Work And Kinetic Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



S3 Amazonaws Com Scschoolfiles 747 Ch 9 4 Gravitational Potential Energy Pdf




Let Us Consider An Equation 1 2 M V2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of



Solutution Set Work And Energy Physics 107




Unit 1 Module 2 Work And Energy




List Of Physics Mnemonics Wikipedia




Work




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics



Chapter 6




Check The Correctness Of Equation 1 2mv2 Mgh Using Dimensional Analysis Method Brainly In




Work Done Against Gravity Cpo Science



Does Gravity Do Work With Step By Step Examples Profound Physics



Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator
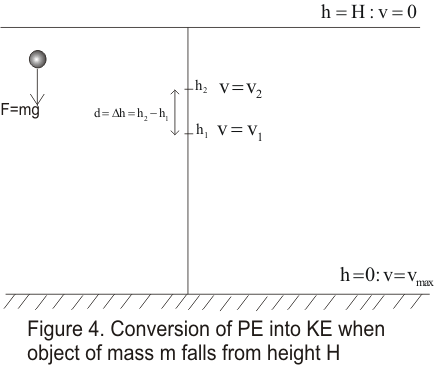



Potential Energy Gravitational Potential Energy
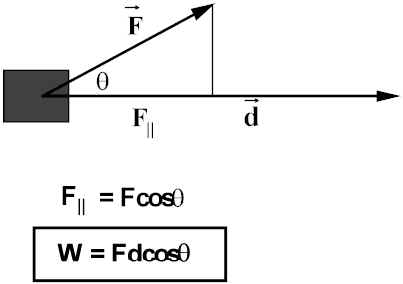



Simple Concepts Involving Work And Energy




Macroscopic Potential Energy Umass Physics 131 Unit 4 Openstax Cnx




Power Formula Derivation Of Power Formula Examples
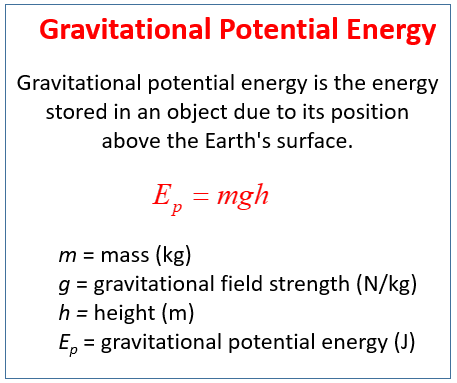



Gravitational Potential Energy Video Lessons Examples Step By Step Solutions




Lesson Gravitational Potential Energy Nagwa




Energy Work And Power Forms Of Energy Mechanical




Htpibreview Ch6 P Mgh T Example Youtube



Www Humbleisd Net Cms Lib2 Tx Centricity Moduleinstance Work and energy worksheet keys Pdf



Work Done By Gravitational Field And Its Calculation Video Dailymotion




The Problem Reads I Understand How W Mgh Force Chegg Com




Mcat Physics Work And Energy Ch 2 Flashcards Quizlet




Prove Potential Energy P E Mgh With Figure Brainly In




Mastering Physics Solutions Chapter 7 Work And Kinetic Energy A Plus Topper



Malaysia Pmr Spm Student S Learning Portal Provides Free Notes E Books References Formula List For Teachers Students For Tuition Or School Study Purposes




P 2 2 1 Forces And Energy P
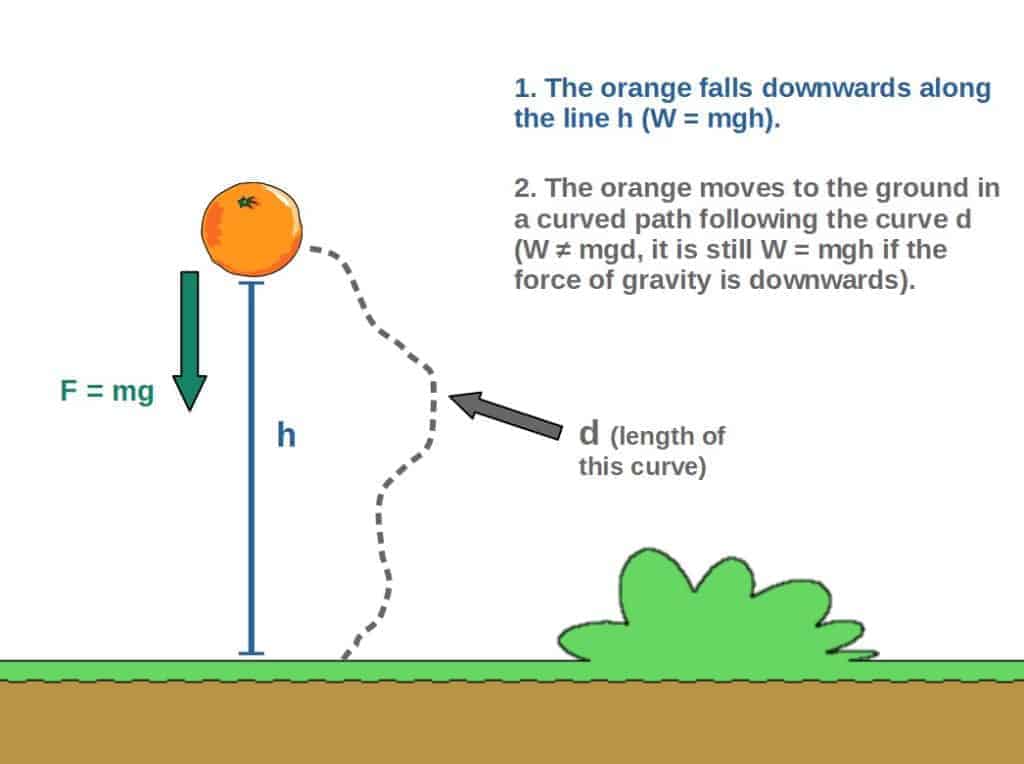



Does Gravity Do Work With Step By Step Examples Profound Physics



How Can We Calculate Absolute Potential Energy As Zero From Its Formula Quora



Physicslab Gravitational Potential Energy



Http Jjphysics Pbworks Com W File Fetch 14 15 Wep Notes Pdf




Motion Revision Part 6 Of 8 Work Done By A Constant Force Energy Transformation Ppt Download




Answers




Potential Energy Geeksforgeeks
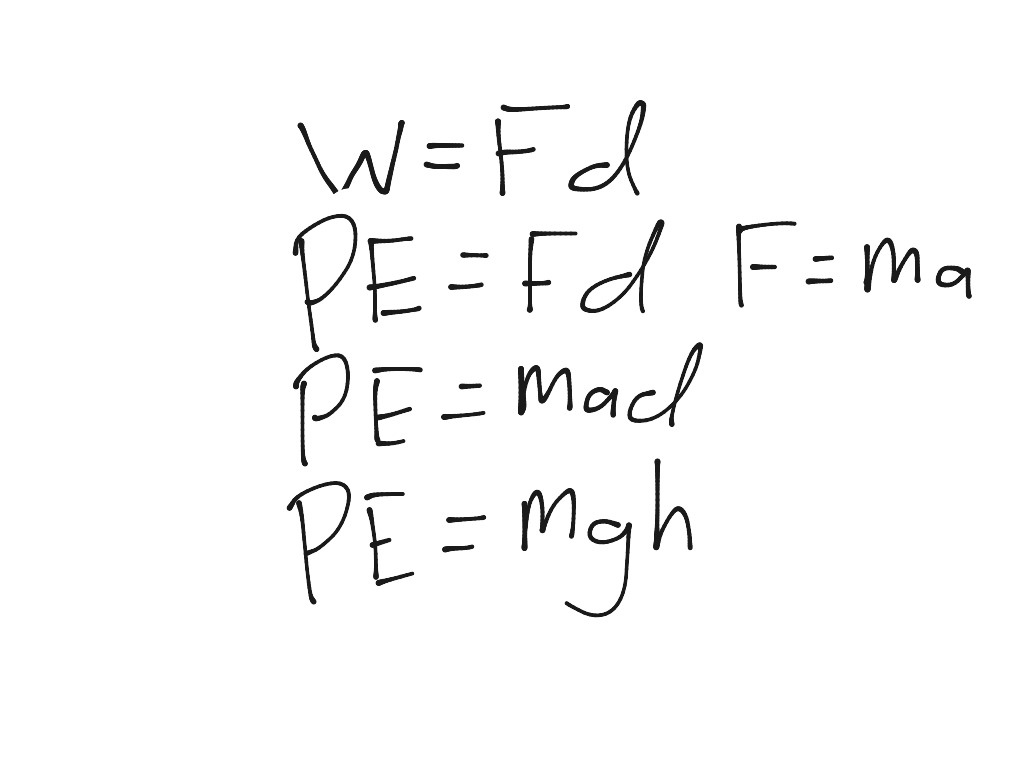



Deriving The Formula For Potential Energy Science Physics Kinematics Showme




Work Done By Gravity Path Independent Video Khan Academy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿